Performance Advantages of Allstar Material's Thermoplastic PI
Exceptional High-Temperature Performance
The high-temperature resistance of Thermoplastic Polyimide (TPI) is exceptionally outstanding. Its key indicator, the Glass Transition Temperature (Tg), typically ranges from 250°C to 350°C.
Simultaneously, its Continuous Use Temperature (CUT) generally reaches 240°C to 300°C, allowing for long-term stable operation at such high temperatures without significant loss of its critical mechanical, electrical, and other properties. This superior thermal stability makes TPI an ideal choice for replacing metals or other high-performance plastics in extreme thermal environments.”

Melt Processability
Unlike traditional thermosetting polyimides, TPI can melt and flow at high temperatures. This allows it to be processed using standard thermoplastic methods such as injection molding and extrusion. Processing temperatures are typically high, generally in the range of 350°C to 420°C, depending on the grade. This enables TPI to be used for manufacturing precision components with complex geometries, expanding its application range and allowing for high-volume, cost-effective production, which is difficult to achieve with traditional PI.

Excellent Mechanical Strength and Wear Resistance

Good Chemical Inertness and Radiation Resistance
TPI materials effectively resist erosion from various organic solvents, fuels, oils, weak acids, and weak bases, maintaining stable performance in complex chemical environments. In terms of radiation resistance, the TPI structure can withstand high doses of ionizing radiation with minimal performance degradation. Typically, TPI materials can tolerate cumulative gamma (γ) ray doses up to 1 x 10⁷ Gy (Gray) or 1 x 10⁹ Rad (rad) while still retaining most of their critical mechanical properties. This makes them an ideal choice for applications in the nuclear industry, aerospace, and medical sterilization involving radiation exposure. (Please note: Specific performance regarding chemical compatibility and radiation resistance will be influenced by factors such as grade, temperature, exposure time, and type of radiation.)
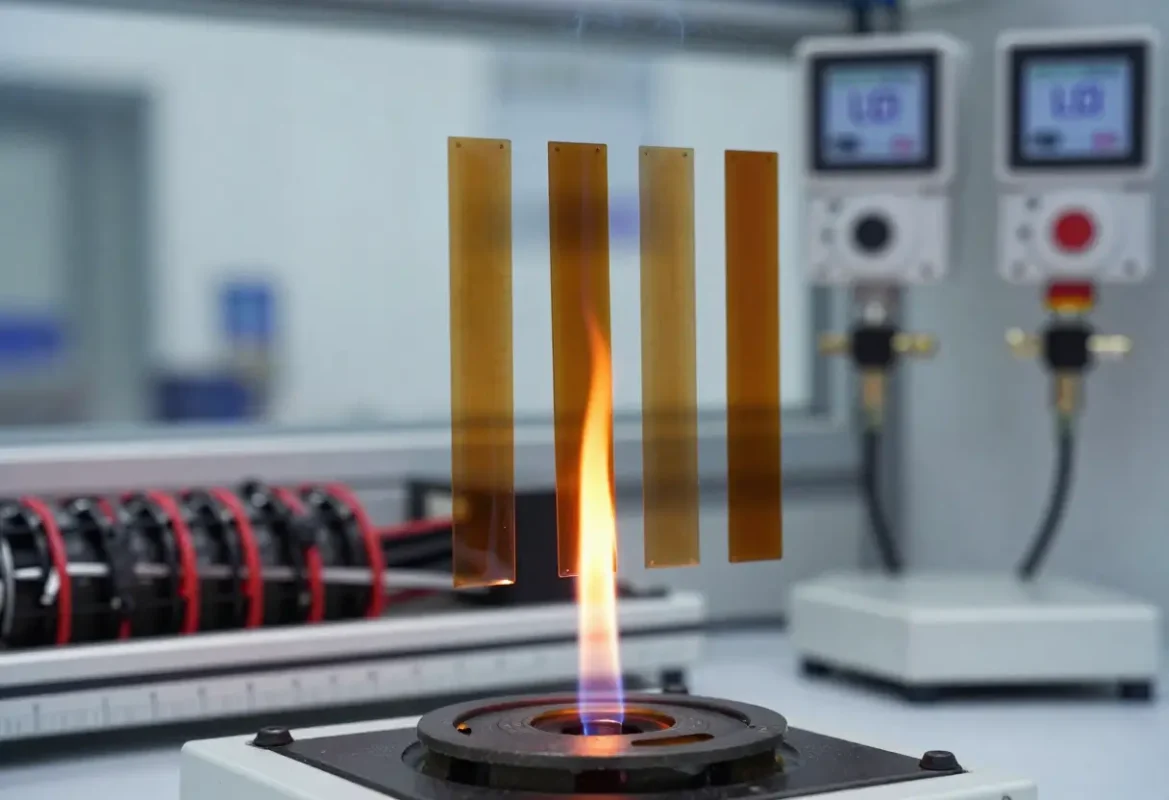

Flame Retardancy
UL 94 Rating: Unreinforced TPI grades can typically achieve a UL 94 V-0 rating, even at thin test thicknesses (e.g., 0.8 mm or 1.6 mm). This signifies that the material self-extinguishes rapidly in a vertical burn test with no dripping. Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI): TPI’s LOI values are usually high, generally exceeding 35% (specific values vary by grade, some can reach over 40%). A high LOI indicates that the material is not easily combustible in air and requires a higher oxygen concentration to sustain combustion. Low Smoke and Toxicity: When burned, TPI produces relatively low smoke density and releases fewer toxic or corrosive gases, which is crucial for aerospace, public transportation, and confined space applications.
Electrical Insulation
Processing of Allstar Material's Thermoplastic Polyimide (TPI)
The processing of Allstar Material's Thermoplastic Polyimide (TPI) from our factory primarily utilizes standard thermoplastic techniques, including injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding. Due to its high melting temperature, the processing window is typically set between 350°C and 400°C.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is one of the most efficient methods for producing complex-shaped TPI parts. The process involves feeding pre-dried TPI pellets (typically dried at 150°C – 200°C for several hours to remove moisture) into the barrel of an injection molding machine. In the barrel, TPI is heated above its melting temperature (usually in the 350°C – 400°C range) by the rotation of the screw and external heaters. The molten TPI is then injected under high pressure into a precision-engineered mold cavity. To ensure parts achieve good crystallinity (if the grade is semi-crystalline), dimensional stability, and low internal stress, the mold temperature needs to be maintained at a high level, generally 150°C – 230°C.
Due to TPI’s high melt viscosity, high injection pressures and appropriate injection speeds are usually required to completely fill the mold cavity. After the molding cycle, parts are ejected. Sometimes, annealing is performed to further optimize performance. This process requires injection molding equipment with high-temperature resistant barrels, screws, and molds.”
Extrusion
TPI Compression Molding
Thermoplastic Polyimide (TPI) Applications
Thermoplastic Polyimide (TPI), with its excellent comprehensive properties, is widely used in several demanding fields. The following are some major application areas:
Aerospace & Defense:
Engine Components: Used to manufacture some non-structural high-temperature components in jet and rocket engines, such as insulation parts, low-friction bushings, and seal rings.
Connectors & Cables: Due to its excellent electrical insulation, high-temperature resistance, and flame retardancy, used for manufacturing high-performance connectors, sockets, and insulation layers or sheaths for special wires and cables.
Structural Parts & Interiors: Used for internal parts and brackets in aircraft or spacecraft in applications requiring lightweight, high-strength, and flame-resistant properties.
Electrical & Electronics:
Connectors and Sockets: Especially those needing to withstand high temperatures (like reflow soldering), high frequencies, or requiring high dimensional stability, such as IC Test Sockets. Coil Bobbins & Insulators: Used for coil bobbins, insulators, and insulation components operating in high-temperature or high-voltage environments. Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) Substrates: TPI film can be used as a substrate or coverlay for flexible printed circuits requiring higher temperature resistance. Semiconductor Manufacturing: Used for parts in wafer handling, testing, and packaging processes, such as vacuum pen tips, fixtures, and insulation gaskets, leveraging its high-temperature resistance, low outgassing, and plasma resistance.
Industrial Equipment & Machinery:
Bearings & Bushings: Especially for sliding bearings, bushings, thrust washers, and seal rings in high-temperature, high-speed, high-load, or chemically corrosive environments, utilizing their excellent wear resistance, low friction, and high-temperature performance.
Pump & Valve Components: In chemical, oil, and gas industries, used to manufacture corrosion-resistant, high-temperature resistant pump body parts, valve seats, and seals.
Compressor Components: Such as piston rings and guide rings, capable of operating under oil-free lubrication or high-temperature conditions.
Wear Parts: Used as wear strips, guide rails, gears, etc., for various equipment.
Automotive Industry:
Engine & Transmission Systems: Used to manufacture high-temperature, wear-resistant components like thrust washers, seal rings, and bearing cages.
Electrical Systems: Applied in sensor housings, connectors, etc., requiring high-temperature resistance.